This is part two of our answer to a question about soccer set pieces. In the first section, we covered what a set piece is, how valuable they are, and delved into why some teams practice them more than others. In this section we’ll describe in some detail the major types of set pieces.
Dear Sports Fan,
What is a set play in soccer?
Thanks,
Kimberly
Dear Kimberly,
Soccer has a variety of types of set pieces. Now that you know generally what a set piece is and why it is unique and important, it’s time to describe the different types of set pieces. Let’s take a look at each one.
Corner Kick
When the ball goes out of bounds over the goal line and the last player to touch it was on the defensive team, a corner kick is given. The ball is put at the corner (no kidding) of the field and the offensive team gets to kick it in from there. Corner kicks are one of the most valuable set plays for the offense. It’s a free chance to swing a ball, in the air, into the penalty box right near the goal and try to head it in. Teams that get a corner kick frequently try to increase the odds of their team being the first to hit the incoming corner kick in the air but getting all of their tallest players in there. Since defenders are usually the biggest players on the field, this often means that some defenders move up when there is a corner and shorter offensive players move back to replace them. As a former defender, I can say that this is good fun for the defense. It also leaves the team that gets the corner kick a little vulnerable to a quick counter-attack since their best defensive players are all the way up near the goal they are trying to score on.
Sometime, the team with the corner kick will choose to play a “short corner”. Instead of a crossing the ball into the penalty area, one player on the offensive team will spring towards the corner of the field to receive a short pass from their teammate with the ball. Usually, this is a tactic to create a more favorable angle to cross the ball from as opposed to a complete rejection of the idea of crossing the ball. I have a personal grudge against the short corner and tend to get pretty upset when I see teams do it. I don’t think the benefit of the better angle is worth the cost of potentially losing the chance to send a ball into the box.
Goal Kick
A goal kick is what happens when the ball goes over a goal line and it was last touched by a player on the attacking team. The ball is placed within the smaller of the two rectangles around the goal, called the goal box, and a player (usually the goalie) has a free chance to kick the ball back into play from there. In professional or high-level amateur play, this set piece is not all that interesting or important. Goalies are able to pass the ball accurately to a defensive player or boom the ball halfway down the field (or more!) to an offensive player. In youth soccer, the goal kick is a little more exciting because kids usually cannot kick the ball as far or as well. In youth soccer, I remember the offensive teams lining up eagerly on the edge of the larger rectangle around the goal, the penalty box, and trying to intercept the goal kick and quickly transition to offense.
Throw In
When the ball goes out of bounds on one of the sidelines (also called touchlines) the team that did not touch the ball last gains possession of the ball and is granted a throw in. The throw in is exciting because it’s the one time when non-goalie soccer players get to touch the ball with their hands! Eh… actually, it’s not such a big deal. Any soccer player worth her weight, even in some non-precious metal like tin, is able to kick the ball much farther, faster, and more accurately than they can throw it. Most throw ins therefore become a quick exercise in maintaining possession. Usually, the player throwing the ball in will look for a teammate running towards him and throw the ball to that person who quickly taps it back to the thrower who is then free to do whatever they want with it. It’s all about getting the ball back into the field and in control of your team. When an offensive team has a throw in near the goal their trying to score on, close to where they would take a corner kick from, they may choose to treat the set piece like a corner that just has to be thrown instead of kicked. There’s usually someone on each team who can do a “long throw” and send the ball into the center of the field with as much pace as possible.
There are rules about how the ball should be thrown: Both feet have to be on the ground when the ball leaves the throwers hands. The ball must be held with two hands and the two arms have to move in parallel to eliminate putting tricky spin on the ball. You rarely ever see referees enforce these rules at the professional level but in youth soccer throw in fouls get called all the time.
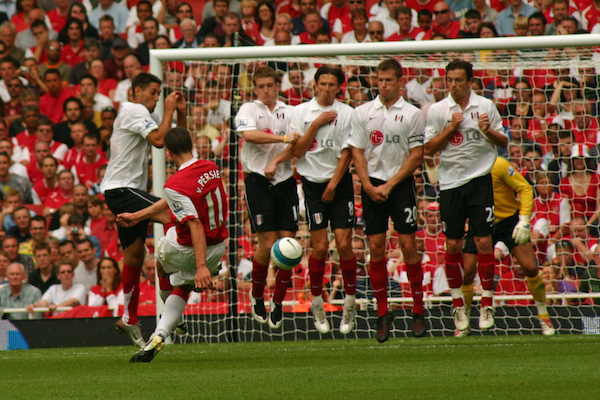
Free Kicks
When a foul is called in the course of play, the ref stops play and the ball is placed at the spot of the foul. The team whose player has been fouled (or dove convincingly…) gets to put the ball back into play from that spot. When a foul is called anywhere far from the goal the team is trying to score on, the free kick is usually a quick deal. Simple possession of the ball is worth more than the chance to kick the ball a long way without being guarded, so teams with free kicks in their own half of the ball just pass it to an open teammate and keep the game moving. A free kick anywhere in the offensive third of the goal is one of the most valuable moments in the entire soccer game. Teams that get a free kick like this usually take their time, and then execute. Meanwhile, defensive teams try to counteract this by setting up themselves. Some defenders will take responsibility for preventing an offensive player from getting onto the end of a free kick pass while others set themselves up ten yards from the ball in a wall to prevent an easy free kick shot.
Free kicks are divided into two types: direct and indirect. Direct kicks are most common and there’s no restriction on what offensive teams can do with them. Indirect kicks are given for less serious fouls that violate a technical rule as opposed to a safety rule. Examples of fouls that result in an indirect kick are being offside, insulting a ref, or if the goalie touches the ball with her hands when she’s not allowed to. Indirect kicks are the same as direct kicks except two players have to touch the ball before a goal is allowed to be scored. Teams either use indirect kicks to pass the ball, often like a corner kick, or they set up two players near the ball and convert the kick into a direct kick by having one player touch the ball a tiny bit and then the other shoot the ball.
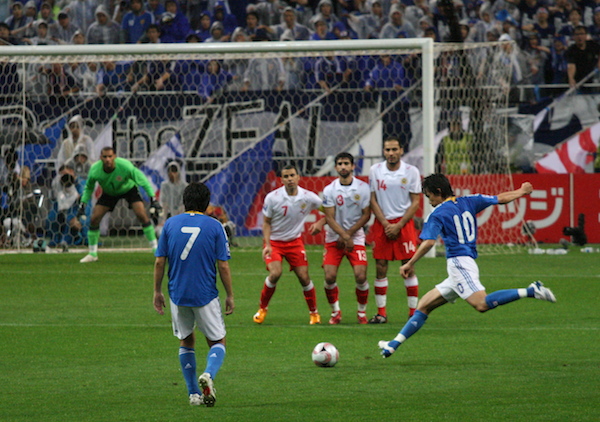
Penalty Kick
A penalty kick is a special type of set piece. The ref calls for a penalty kick when a foul which otherwise would result in a direct free kick is committed by a team within their own penalty box. The penalty kick is extraordinarily valuable. It’s like nothing else in sports, really. 85% of penalty kicks result in goals. That’s better than the league average for a free throw in the NBA! Okay, sure, the extra point in football is made close to 100% of the time but one goal in soccer is worth so much more than one point in football. The penalty kick is unlike any other set piece in soccer — so much so, that most people probably don’t think of it as a set piece at all. If you want to learn more about it, read our article all about penalty kicks.
There you go — that’s probably more than you bargained for about set pieces in soccer,
Ezra Fischer