Dear Sports Fan,
What does it mean to be “mathematically eliminated” from something?
Thanks,
Will

— — —
Dear Will,
“Mathematically eliminated” is one of those phrases that you hear often in sports but not in too many other contexts. A team or player that is mathematically eliminated cannot win or qualify for something in any of the possible permutations of future outcomes. This can happen within a game, within a season, or within a tournament or playoffs. You’re probably hearing it a lot now because the NFL season is in its 16th of 17 weeks and teams are being mathematically eliminated left and right. Let’s explore some of the common forms of mathematical elimination.
Mathematically eliminated from qualifying for the playoffs
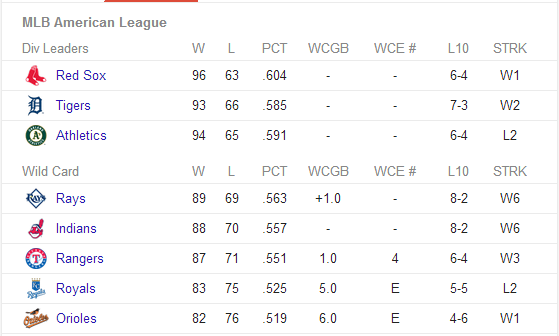
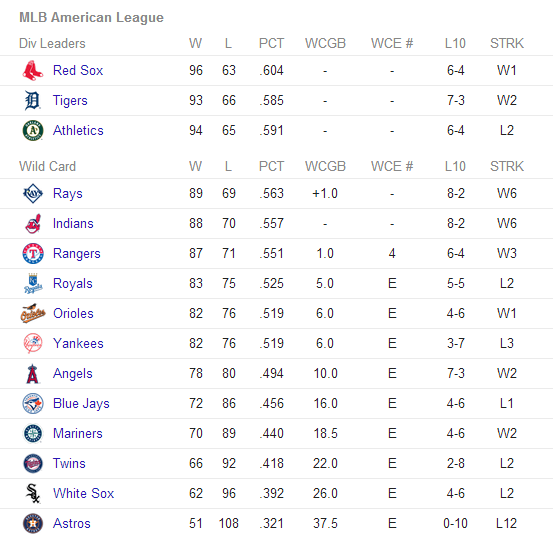
A team is mathematically eliminated from the playoffs when no possible permutation of wins and losses in all the remaining games in a season result in them qualifying for the playoffs. This is a surprisingly high bar. For instance, with only two games remaining, the 6-8 Pittsburgh Steelers are still alive for a playoff spot according to CBS. What would have to happen for them to qualify? According to the Altoona Mirror, the Steelers need “about 10 things to happen” and the chances of them all happening are around 100 to 10. They detail all of the necessary dominoes here. Stranger things have happened, for sure, but it certainly stretches the imagination to think that all ten of the items are going to happen just the way the Steelers need them to to make the playoffs. One could say they have been plausibly eliminated but as long as there is a single path for them to make the playoffs, the team and their fans will keep hoping.
Other forms of mathematical elimination — shootout edition
Although the phrase “mathematically eliminated” is almost only ever used about the playoffs, as explained above, there are other types of mathematical elimination in sports. A shootout is one example. In many hockey and soccer leagues, if a game is tied the teams play timed overtime periods. If it is still tied after that, the game is decided by a series of one-on-one contests between a player and a goalie. This is called a shootout. The shootout is arranged like you or I would play odds-and-evens or rock-paper-scissors. In the NHL it is a best of three, in Major League Soccer and international soccer, it is a best of five. Both of these contests work in frames — first one team goes, then the other, repeat. This leaves the door open for mathematical elimination within the shootout. If a team has scored more goals than the other team has remaining shots (in hockey, a team would have to score the first two with the other team missing the first two. In the longer soccer shootout, there are more ways for this to happen,) it’s impossible for that second team to win. In this case, the game is over. The final shots cannot possibly have an effect on the outcome of the game, so they aren’t taken.
Other forms of mathematical elimination — playoff edition
The same logic found in the shootout is also used during the best out of five or seven game series found in the NHL, NBA, and MLB playoffs. Earlier this year, we answered the question, “what is a sweep?” A sweep is when a team wins the first three games of a five game playoff series or the first four in a seven game series. In either case, this is a decisive victory because the winless team doesn’t have enough games in the series left to have any chance of winning the majority of games. They are mathematically eliminated from the playoff series. Like the shootout, the final games of the playoff series are not played because they could not possibly have any affect on the outcome.
Other forms of mathematical elimination — end of game edition
Mathematical elimination can also happen during a game in some sports. Baseball games and tennis matches are organized like little miniature playoff series or shootouts. Tennis matches are organized into best-of-three or five set contests. Each set is organized into best of thirteen game contests. In each of these layers, if a player mathematically eliminates their opponent by winning seven games or two or three sets, the theoretical remainder of the set or match is not played. Baseball is roughly the same. The contest is divided into innings that each have a first half (or top as it’s called) and second half (bottom.) The away team bats in the top of the inning and the home team in the bottom. In the ninth and final inning, if the home team is winning at the end of the top of the inning, the game is over. There is no way for the road team to score any runs in the half of the inning when they are in the field, so there is no reason for that half-inning to be played. They are mathematically eliminated from the game.
Football is perhaps the most curious sport when it comes to in-game mathematical elimination. Football isn’t organized into innings or frames or sets and matches. It’s one continuous game but a wrinkle in the rules makes it possible for a team to (more or less) be mathematically eliminated. In football, the clock either runs or doesn’t run between plays based on the outcome of the play. If there is an incomplete pass, a player runs out of bounds with the ball, or there is a penalty, the clock stops. When a player is tackled with the ball within the boundaries of the field, the clock keeps running, and only a time-out can stop it. If a team is winning AND they have the ball AND the opposing team has no time-outs left, the team with the ball can simulate being tackled on the field by snapping the ball to the quarterback and having him kneel down. This keeps the clock running for up to 40 seconds between each play and a team with the ball can do this three times consecutively. Teams use this strategy as a form of mathematical elimination. If there is less time left in the game (40 x 3 = 2:00) than a team can waste by kneeling, the game is effectively over.
This is really only an almost mathematical elimination because the team with the ball could mistakenly fumble the ball during the snap and if the other team picked it up, they could have a chance of winning. Teams on the losing side of the football game almost never even try to make this happen because it’s so unlikely that it seems lacking in common and professional courtesy to shoot for it. In my memory, the only coach to instruct his team to go for this was former Rutgers head coach, Greg Schiano. Trust my alma mater to foster this type of radical (and rude) thinking! All jokes aside, mathematical elimination is a tricky thing for sports leagues to figure out because it undermines a basic motivation for teams and players: once you have been mathematically eliminated, what is the purpose of continuing to try? This problem is most common when teams have been eliminated from the playoffs during a season and, because the order they get to draft players for next season in is set in inverse (or roughly inverse) order of their record in this season, they have an incentive to lose as many games as possible. This is called tanking and is a scourge to the sports world roughly equal to the flu in the normal world or sarcoidosis on House.
It’s a scourge for another post though, so until then, happy holidays!
Ezra Fischer